What is the Diabetes Honeymoon Phase?
The ‘honeymoon phase’ in diabetes is a period following the initial diagnosis and treatment of diabetes, particularly type 1, and sometimes type 2. During this phase, individuals may experience a temporary reduction in their insulin needs or improved blood sugar control. This can lead to a feeling of improved health and well-being, often mistaken for a cure. It’s crucial to understand that the honeymoon phase is not a cure, but rather a temporary reprieve before the disease progresses. It presents a unique window of opportunity to establish healthy habits and a strong foundation for long-term diabetes management. This phase can vary in duration, and not all individuals with diabetes experience it.
Understanding the Definition
The term ‘honeymoon phase’ refers to the period after the initial diagnosis and treatment of diabetes where blood glucose levels are easier to manage. This is due to the pancreas still producing some insulin in type 1 diabetes or improved insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes. The body’s own insulin production, combined with the initial treatment, leads to better control of blood sugar levels. This stage may seem like a return to normal health, but it is essential to remember this phase is a temporary state and not a sign of a cure. This improved control often reduces the need for medication or insulin doses, making it seem like diabetes is less of a daily concern.
Duration and Timeline

The duration of the honeymoon phase is variable and differs from person to person. It can last for a few weeks, several months, or sometimes even longer, but it is not permanent. Several factors influence the length of this phase, including the age of the individual, the initial severity of the disease, and the effectiveness of the initial treatment. The honeymoon phase ends when the pancreas gradually loses its ability to produce insulin, and/or insulin resistance increases, causing blood sugar levels to rise again. Being aware of the potential duration and the eventual transition back to the need for active management is essential for both patients and their caregivers.
Who Experiences the Honeymoon Phase?
The honeymoon phase is most commonly associated with type 1 diabetes, although it can also occur in some individuals with type 2 diabetes. The impact and experience of the honeymoon phase vary greatly, depending on the type of diabetes and individual circumstances. It’s crucial to understand the specificities of each type of diabetes to manage expectations and tailor treatment plans.
Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, the honeymoon phase occurs after the initiation of insulin therapy. This phase is characterized by a period of improved blood sugar control because the remaining beta cells in the pancreas continue to produce some insulin. During this phase, individuals might need a reduced insulin dosage or experience fewer fluctuations in blood glucose levels. The duration of the honeymoon phase in type 1 diabetes can range from a few weeks to several months, and the experience varies from person to person. It’s essential for people with type 1 diabetes to understand that this phase is temporary and does not indicate a reversal of the disease.
Type 2 Diabetes

While less common than in type 1 diabetes, the honeymoon phase can also occur in individuals with type 2 diabetes, particularly after lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise or initiation of medications. In type 2 diabetes, the honeymoon phase might be characterized by improved insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control, often resulting in reduced medication needs. The body’s increased ability to use insulin effectively leads to lower blood sugar levels. The duration of this phase in type 2 diabetes varies, and it’s often shorter than the honeymoon phase in type 1 diabetes. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and adhering to prescribed medications is critical for managing type 2 diabetes effectively.
5 Key Facts About the Diabetes Honeymoon Phase
Understanding the following key facts will help you navigate the diabetes honeymoon phase more effectively and prepare for the long-term management of your condition.
Fact 1 Reduced Insulin Needs
One of the hallmarks of the honeymoon phase is a significant reduction in insulin requirements for those with type 1 diabetes. As the body’s insulin production recovers partially, the need for external insulin decreases. This can lead to lower insulin doses or, in some cases, a temporary suspension of insulin therapy. It’s important to carefully monitor blood sugar levels to avoid both high and low blood sugar episodes during this phase. The reduced insulin needs reflect the temporary improvement in the body’s ability to regulate blood glucose.
Fact 2 Improved Blood Sugar Control
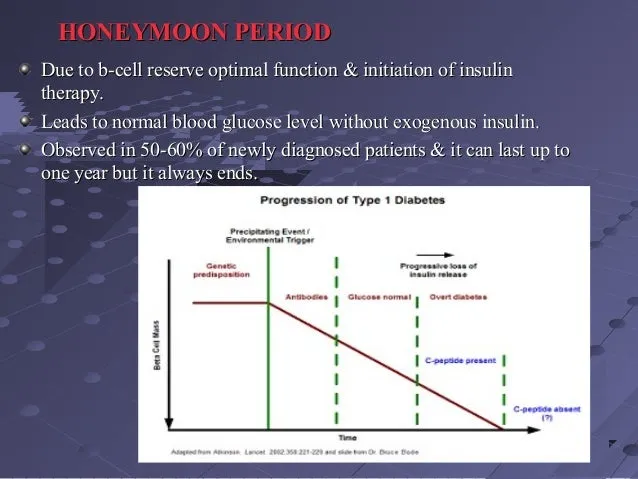
During the honeymoon phase, individuals often experience better blood sugar control, with fewer fluctuations and lower average glucose readings. This improvement results from the combined effect of any remaining insulin production and the initial insulin therapy or medication. Consistent blood sugar monitoring helps identify patterns and maintain optimal glucose levels, which reduces the risk of both short-term and long-term complications. Improved control provides a valuable opportunity to establish and reinforce healthy habits.
Fact 3 Potential for Misinterpretation
The honeymoon phase can sometimes be misinterpreted as a cure or remission of diabetes. This misinterpretation can lead to a relaxation of necessary lifestyle adjustments and treatment adherence. It is critical to understand that the honeymoon phase is temporary. Education and support from healthcare professionals are vital to manage expectations and stay focused on long-term diabetes management. Misunderstanding this phase may lead to poorer long-term outcomes.
Fact 4 The Honeymoon Phase is Not a Cure
It is essential to understand that the honeymoon phase is not a cure. Diabetes remains a chronic condition that requires ongoing management, even when blood sugar control is good. Eventually, the body’s insulin production will decrease, or insulin resistance will increase, and the need for medication or insulin will return. This underscores the importance of continuous monitoring, healthy lifestyle choices, and adherence to treatment plans. Recognizing that the honeymoon phase is temporary helps prevent complacency and promotes proactive diabetes management.
Fact 5 Individual Variability

The experience of the honeymoon phase varies greatly from one individual to another. Some people might experience a long honeymoon phase, while others might have a shorter one. The duration depends on a variety of factors, including age, the severity of the initial diabetes diagnosis, and the specific treatment plan. This variability emphasizes the importance of personalized care and close monitoring. Healthcare professionals can provide tailored guidance to help individuals manage their diabetes effectively throughout this phase and beyond. Regular check-ups, consistent monitoring, and personalized treatment plans are key.
Managing the Diabetes Honeymoon Phase
Managing the honeymoon phase effectively involves careful monitoring, consistent healthy habits, and regular communication with healthcare providers. The goal is to make the most of this period while preparing for the future. A proactive approach can help individuals maintain good health and minimize complications.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial during the honeymoon phase. This involves checking blood sugar levels at different times of the day, such as before meals, after meals, and at bedtime. This allows individuals and their healthcare providers to track the fluctuations in blood sugar and adjust the treatment plan accordingly. Keeping a detailed record of these readings helps in identifying trends and making informed decisions about insulin dosages, medication, or lifestyle adjustments. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) can provide even more comprehensive insights, offering real-time data and alerts.
Importance of Regular Doctor Visits

Maintaining regular appointments with your doctor or diabetes specialist is vital. During these visits, healthcare providers can assess your blood sugar control, review your treatment plan, and address any concerns. Regular check-ups allow for timely adjustments to medication or insulin dosages as the honeymoon phase evolves. They also provide an opportunity for education and support, helping individuals manage their diabetes effectively. It’s crucial to discuss any changes in your blood sugar levels or symptoms during these visits.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting and maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role during the honeymoon phase and beyond. This includes following a balanced diet with controlled carbohydrate intake, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress levels. Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, which in turn helps regulate blood sugar levels. A healthy diet, rich in fiber and low in processed foods and sugary drinks, aids in maintaining stable glucose levels. Stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can also contribute to improved blood sugar control. Consistent healthy habits are important.
What Happens After the Honeymoon Phase?
Eventually, the honeymoon phase will end, requiring adjustments to the treatment plan. Being prepared for this transition is critical for continued effective diabetes management. Understanding the changes to expect and being proactive about them can help individuals maintain good health.
Preparing for Insulin Therapy or Adjustments
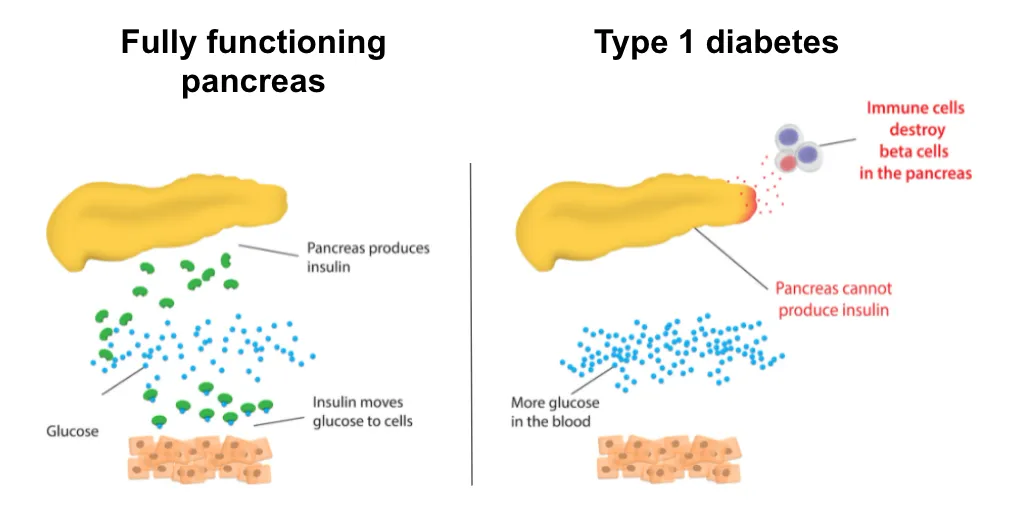
As the honeymoon phase wanes, the need for insulin therapy or adjustments to existing medications will likely increase. This is due to the gradual decline in the body’s own insulin production or worsening insulin resistance. Working closely with your healthcare team to monitor blood sugar levels and determine the appropriate insulin dosage or medication changes is essential. Regular check-ups, monitoring, and consistent communication with the doctor can help in making these adjustments smoothly and effectively. Preparing mentally and practically for increased medication needs is a part of long-term management.
Long-Term Diabetes Management
Long-term diabetes management involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and taking prescribed medications as directed. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor blood sugar levels, assess any complications, and adjust the treatment plan. Long-term diabetes management is about adopting sustainable habits and working in partnership with healthcare providers to maintain good health and prevent or minimize complications. Education and support are key.
